🧠 Java Memory Management
📋 What is Memory Management in Java?
When you run a Java program, Java needs memory to:
- Store objects
- Run methods
- Store variables
- Handle class information
Mnemonic to Remember: JVM is like a "Janitor Vacuuming Messes" – it cleans up automatically so you don't have to worry about forgetting to free memory.
🏠 Real-Life Example
Imagine your computer is a house:
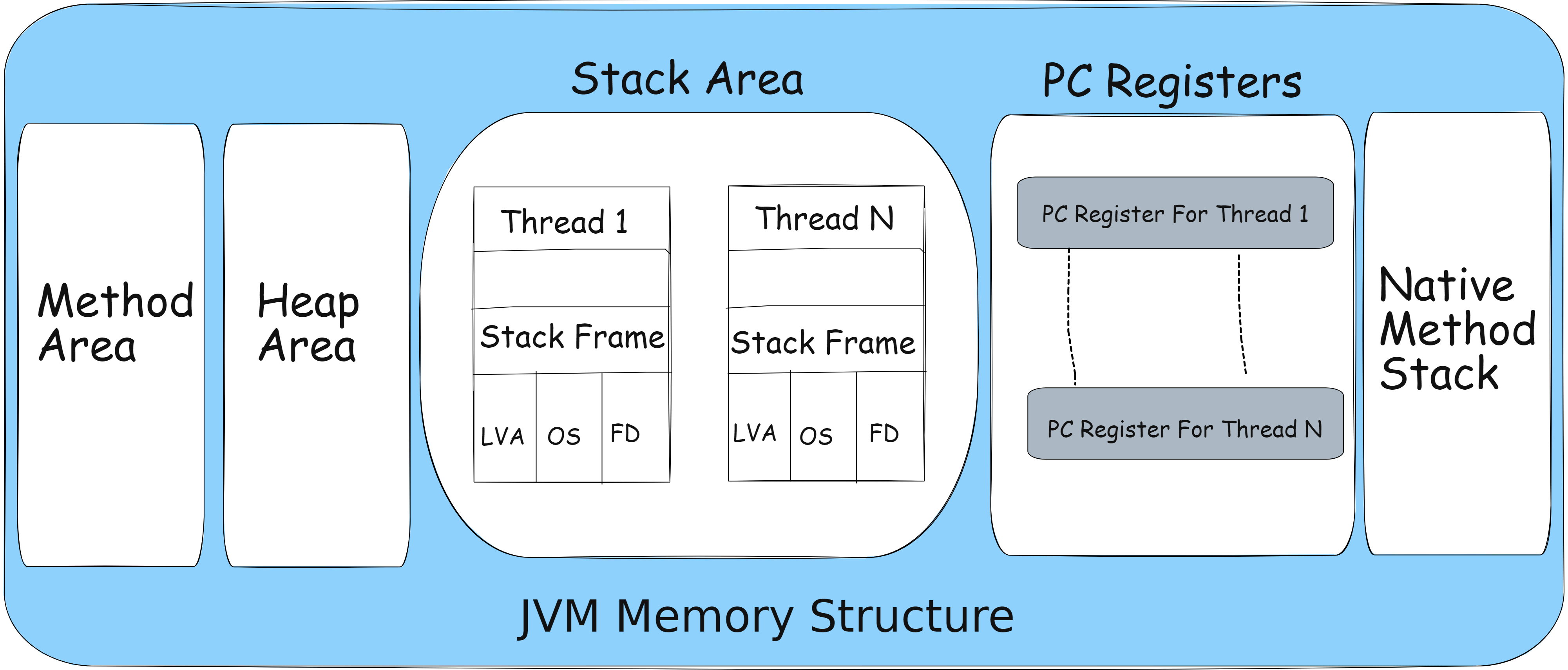
- Heap = Big cupboard shared by everyone — stores all objects (think of it as a party hall where objects come and go).
- Stack = Small desk each person (thread) uses — stores local variables and method info (like a stack of plates, last in first out).
- Method Area = Library — stores blueprints (class info, static data).
- PC Register = Pointer showing what you're currently doing.
- Native Stack = A side tool area if you call C/C++ functions.
Easy to Remember: Heap for "Heavy Objects", Stack for "Short-term Stuff".
📦 Java Memory Areas (Explained Simply)

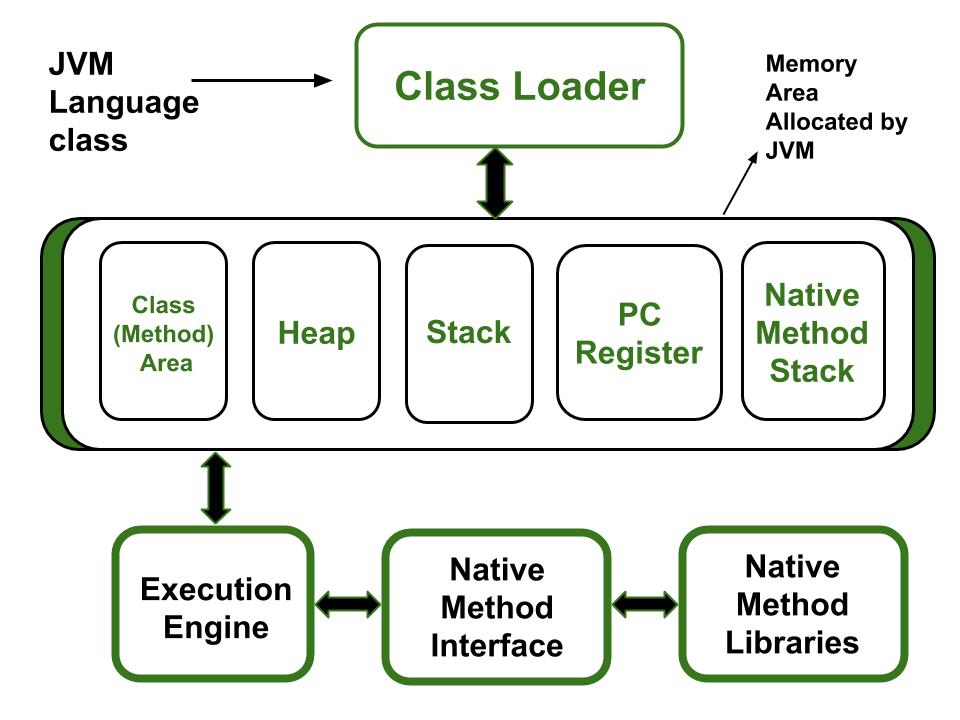

1. Heap Memory (Main Storage)
- Stores:
- All objects created using
newkeyword - Instance variables
- Runtime constant pool (part of Method Area)
- String Pool (special memory area inside Heap)
- All objects created using
- Shared by: All threads
- Cleaned by: Garbage Collector (GC)
- Divided into:
- Young Generation: Newly created objects (Eden + Survivor spaces) – most objects die young, like butterflies.
- Old Generation: Long-lived objects – survivors promoted here.
- Metaspace (Java 8+): Class metadata, method info – replaced PermGen.
Mnemonic: Heap = "Huge Elderly Area for Persistent Stuff" (Young for new, Old for survivors).
String name = new String("Deepak");
👉 Result:
One "Deepak" in String Pool + another new object in Heap.
String s1 = "Hello"; String s2 = "Hello";
👉 Result: Both s1 and s2 point to the same object in
String Pool, no duplicate created.
String s1 = new String("World");
String s2 = s1.intern();
String s3 = "World";
👉 Result:
s2 and s3 refer to the same object in
String Pool, but s1 is a separate object in Heap.
📌 Important Notes on Heap & String Pool:
- Heap is the biggest memory area in JVM, used for almost all object storage.
- Memory management in Heap is automatic (handled by Garbage Collector).
- String Pool optimizes memory by reusing immutable
Stringobjects. - Too many Strings without pooling can cause OutOfMemoryError.
🔑 About intern()
intern()is a method ofStringclass.- It checks whether the String already exists in the String Pool.
- If it exists → returns reference from the pool.
- If it doesn’t exist → adds the String to the pool and returns that reference.
String x = new String("Java");
String y = x.intern();
String z = "Java";
System.out.println(x == y); // false
System.out.println(y == z); // true
👉 Why use intern()?
- Helps save memory by avoiding duplicate String objects.
- Improves performance when many identical Strings are used (e.g., large text processing, XML/JSON parsing).
- But: Excessive interning may increase GC pressure (trade-off).
2. Stack Memory (Per Thread)

- Stores: Local variables, method calls
- Each thread gets: Its own stack
- Cleared when: Method ends
Mnemonic: Stack = "Swift Temporary Area for Calls and Keywords" (LIFO like a stack of books).
int a = 10;
👉 Result: 'a' is a local variable, stored in Stack
3. Method Area / MetaSpace (Blueprints)
- Stores: Class definitions, static variables, method names
- Loaded: Once per class
Mnemonic: Method Area = "Master Archive for Templates and Statics".
static int collegeCode = 123;
👉 Result: 'collegeCode' is stored in the Method Area
4. PC Register
- Keeps track of which line in the method is being executed
- Each thread has one
Mnemonic: PC Register = "Personal Compass for Running Instructions".
5. Native Method Stack
- Only used when you call native (C/C++) code from Java using JNI
Mnemonic: Native Stack = "Niche Space for External Tools".
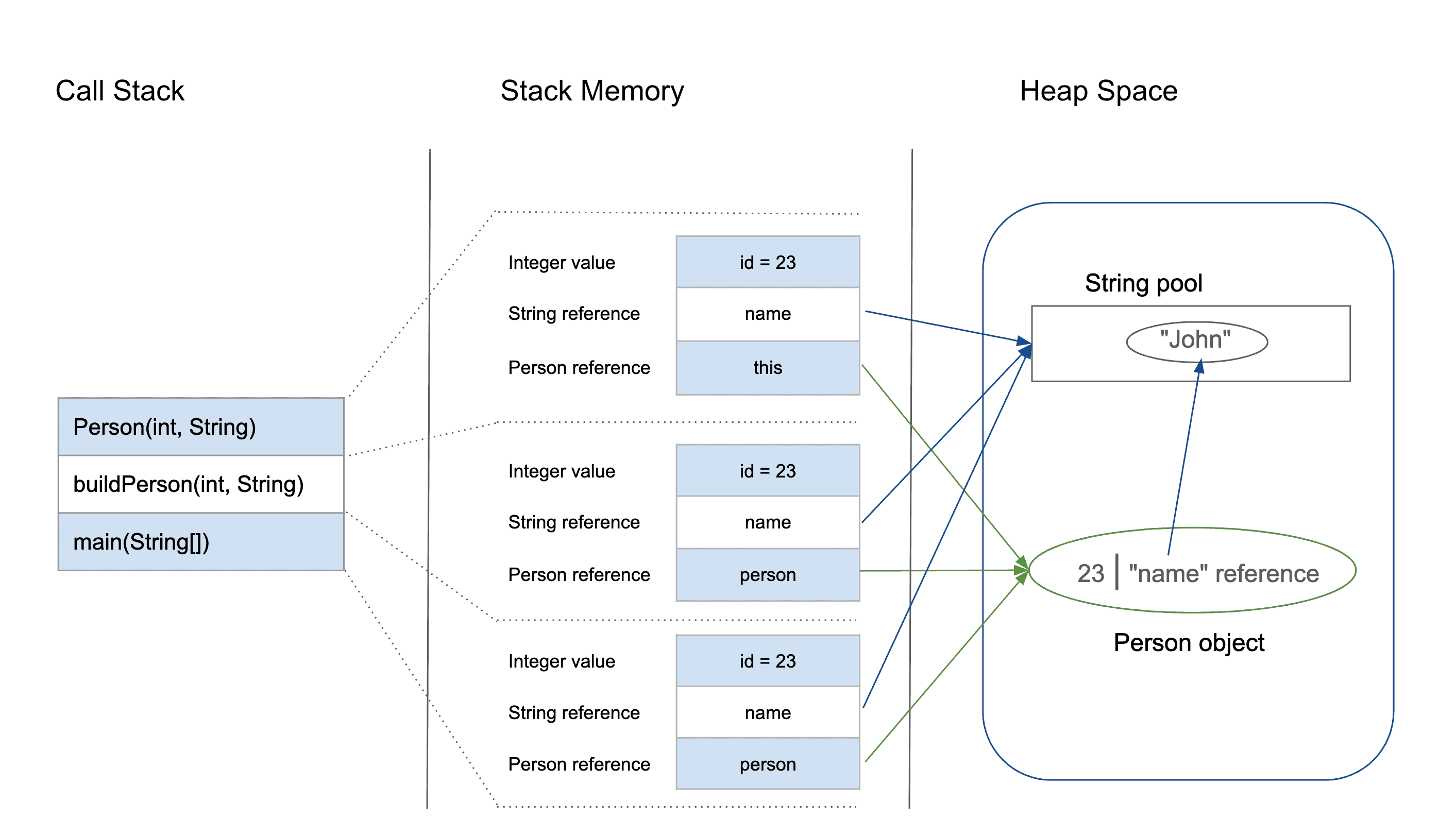
👨💻 Full Example Code + Memory Map
public class Student {
int age = 20; // Stored in Heap
static String school = "ABC"; // Stored in Method Area
public static void main(String[] args) {
int roll = 101; // Stored in Stack
Student s1 = new Student(); // Object in Heap, ref in Stack
}
}
🧠 Memory Map:
| Memory Area | What It Stores |
|---|---|
| Heap | Object s1, instance variable age |
| Stack | roll, reference to s1 |
| Method Area | Class info, school |
🧹 What is Garbage Collection?


- It automatically removes unused objects from the Heap to free memory
- No need to use
free()like in C/C++ - Generational GC: Divides heap into Young (short-lived) and Old (long-lived) for efficiency.
- Stop-the-World: Pauses app during GC – minimize with tuning.
Mnemonic: GC = "Garbage Cleaner" – like a robot vacuum that runs when the room (heap) is messy.
Student s1 = new Student();
s1 = null; // Now the object is not used → eligible for GC
You can suggest GC like this:
System.gc(); // Suggests garbage collection (not guaranteed)
✅ Simple Interview Questions and Answers
| ❓ Question | ✅ Simple Answer |
|---|---|
| What is memory management? | Java automatically allocates and frees memory using JVM. |
| What is the Heap? | Stores objects. Shared by all. Cleaned by garbage collector. |
| What is Stack memory? | Stores method calls and local variables. One per thread. |
| What is garbage collection? | JVM removes unused objects from memory automatically. |
| Where are static variables stored? | In the Method Area. |
| What is stored in Stack vs Heap? | Stack = local vars, refs. Heap = objects. |
| Can you force GC in Java? | You can suggest it using System.gc(), but it's not guaranteed. |
🤔 Interactive Self-Quiz for Interviews
Test your understanding with these expandable questions. Click to reveal answers.
What is the difference between Heap and Stack?
Heap stores objects (shared, GC managed), Stack stores local vars and method calls (per thread, LIFO).
When does an object become eligible for GC?
When it has no live references (null or out of scope).
What are Young and Old Generations?
Young: New objects (Eden + Survivors), Old: Long-lived objects promoted after surviving GC cycles.
What is Stop-the-World?
GC pauses all threads to collect garbage safely.
What are types of references?
Strong (default), Soft (collected when low memory), Weak (collected eagerly), Phantom (for cleanup).
💼 Real Interview Questions on Java Memory Management
These are commonly asked questions in interviews, compiled from sources like Baeldung, Medium, JavaCodeGeeks, and in28minutes.
| ❓ Question | ✅ Answer |
|---|---|
| What Does the Statement “Memory Is Managed in Java” Mean? | Java uses JVM and GC for automatic allocation/deallocation, unlike C where it's manual. |
| What Is Garbage Collection and What Are Its Advantages? | Process to reclaim unused memory. Advantages: No manual free, prevents leaks, focus on logic. |
| Are There Any Disadvantages of Garbage Collection? | Performance impact due to pauses; tune with algorithms like G1 or ZGC. |
| What Is the Meaning of the Term “Stop-The-World”? | Application pauses during GC to allow safe collection. |
| What Are Stack and Heap? What Is Stored in Each? | Stack: Local vars, method calls. Heap: Objects, shared. |
| Describe Generational Garbage Collection. | Heap divided into Young (Eden, Survivors) and Old; minor GC for Young, major for Old. |
| When Does an Object Become Eligible for Garbage Collection? | No live references; null, scope end, or circular without external refs. |
| How Do You Trigger Garbage Collection from Java Code? | System.gc() suggests, but not forced. |
| What Happens When There Is Not Enough Heap Space? | OutOfMemoryError thrown. |
| Is It Possible to “Resurrect” an Object Eligible for GC? | Yes, in finalize() by assigning to static, but only once. |
| Describe Strong, Weak, Soft, and Phantom References. | Strong: Prevents GC. Soft: GC when low mem. Weak: Eager GC. Phantom: For post-GC cleanup. |
| Can Circular References Be GC'ed? | Yes, if unreachable from roots. |
| How Are Strings Represented in Memory? | As objects with char[] and hash; constants in string pool. |
| What Is StringBuilder? Difference from + and StringBuffer? | Mutable string manipulation. + creates new strings. StringBuffer is thread-safe. |
| What is the Java Memory Model? | Defines thread-memory interactions for visibility and synchronization. |
| Describe the different parts of the Java heap memory. | Young (Eden, S0, S1), Old, Metaspace. |
| How does the garbage collector know which objects to collect? | Using marking (reachable from roots) and sweeping. |
| What is a memory leak in Java, and how can it be prevented? | Unused objects retained by references. Prevent by nullifying refs, using tools like MAT. |
| What is the difference between the finalize() method and Cleaner/PhantomReference? | finalize() deprecated, unreliable. Cleaner/Phantom for reliable cleanup. |
| How is Java different from C & C++ in terms of memory management? | Automatic vs manual allocation/free. |
| Why Are Memory Leaks Rare in Java? | Due to automatic GC. |
| What Are Generations in Java Garbage Collection? | Young and Old for efficient GC based on object lifespan. |
| What Are the Types of Garbage Collectors in Java? | Serial, Parallel, G1, ZGC. |
| Why is finalize() Method Deprecated in Java 9? | Unreliable, performance issues; use try-with-resources or Cleaner. |
📝 Final Summary
| Part | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Heap | Stores objects | new Student() |
| Stack | Stores method calls and variables | int a = 5; |
| Method Area | Stores class data, static vars | static int x; |
| Garbage Collection | Removes unused objects | obj = null; |
🎯 Key Points for Interview
- Java uses automatic memory management (no manual free())
- JVM memory has Heap, Stack, and Method Area
- Objects → Heap, Variables → Stack, Class Info → Method Area
- Garbage Collector frees memory automatically
- Understand generations, references, and GC types for advanced questions.